Introduction
In recent studies, arthritis, a term that encompasses over 100 conditions affecting joints and their surrounding tissues, impacts millions globally. [1]

Early recognition of arthritis symptoms is crucial for effective management and treatment. This guide aims to empower individuals with the knowledge to identify arthritis symptoms promptly and understand the treatment options available, ultimately enhancing quality of life.
Understanding the conditions and symptoms of arthritis is essential for individuals to recognize potential issues early on and seek appropriate medical attention. By familiarizing themselves with the various forms of arthritis and their associated symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their joint health and overall well-being.
Understanding Arthritis
Arthritis is characterized by inflammation and pain in the joints. The two most common forms are osteoarthritis, caused by wear and tear of the cartilage, and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder targeting the lining of joints. Key risk factors include genetics, age, previous joint injuries, and obesity. Recognizing these can aid in prevention and early intervention.
Recognizing Arthritis Symptoms
The hallmark symptoms of arthritis include:
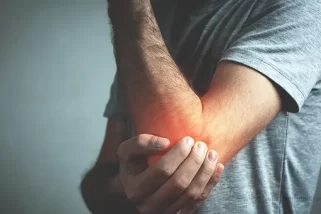
- Joint pain and stiffness: According to research discomfort and rigidity experienced in the joints affected by arthritis. Individuals often notice increased pain and stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity or upon waking up in the morning. This symptom can affect various joints in the body, making movement difficult and uncomfortable. [2]
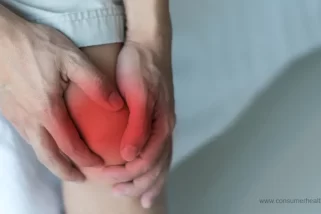
- Swelling and inflammation: Arthritis causes inflammation in the joints, leading to swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected areas. The inflammation is a response by the body's immune system, which can result in discomfort and reduced joint function. Swelling and inflammation are common indicators of arthritis activity and can vary in severity depending on the type and stage of arthritis.
- Reduced range of motion: Arthritis can limit the flexibility and mobility of the joints, resulting in a reduced range of motion. This limitation makes it challenging to perform daily activities such as walking, bending, or grasping objects. Reduced range of motion can significantly impact an individual's quality of life and independence, highlighting the importance of early detection and intervention.
- Other possible symptoms: In addition to joint-related symptoms, arthritis can also manifest systemic symptoms that affect the entire body. These may include fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite. Fatigue refers to excessive tiredness or lack of energy, which can interfere with daily functioning. Fever and loss of appetite may indicate systemic inflammation and involvement beyond the joints, necessitating comprehensive evaluation and management of arthritis.
Elaborating about symptoms, one of the leading chiropractors, Dr. Brent Wells added that in certain types of arthritis, like psoriatic arthritis, symptoms can also include scaly, itchy skin, changes to fingers and toenails, rashes, fever, weight loss, and hair loss in spots or around the hairline.
Identifying Different Types of Arthritis

Common Types of Arthritis. Shutterstock Image
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints. It commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, as well as the hands. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility, particularly after periods of rest or inactivity.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Unlike osteoarthritis, it typically affects joints symmetrically, meaning that if one joint is affected, the same joint on the opposite side of the body is likely affected as well. Symptoms include joint swelling, pain, stiffness, fatigue, and general malaise.
- Psoriatic arthritis: Psoriatic arthritis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that occurs in some people with psoriasis, a chronic skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. Psoriatic arthritis can affect any joint in the body, leading to joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. In addition to joint symptoms, individuals with psoriatic arthritis may experience skin lesions, nail changes, and eye inflammation.
- Gout: Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. It commonly affects the big toe but can also occur in other joints such as the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers. Gout attacks are characterized by sudden and severe pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joint. Triggers for gout attacks include certain foods, alcohol consumption, dehydration, and stress.
Diagnosis of Arthritis
A combination of medical history review, physical examination, imaging tests (e.g., X-rays, MRI), and blood tests are crucial for diagnosing arthritis accurately. Early diagnosis is key to managing symptoms and preventing further joint damage.
Speaking about managing arthtitis, renowned orthopedic surgeon, Dr. Robert McLaughlin II says that it's important to adopt a holistic approach that includes medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. For instance, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation, while targeted exercises can improve joint flexibility and strength. Incorporating low-impact activities such as swimming and cycling can significantly benefit those with arthritis. Furthermore, maintaining a healthy weight is critical in reducing the stress on weight-bearing joints, thus alleviating symptoms.
Treating Arthritis Symptoms
Effective management includes:
- Lifestyle modifications: Balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate symptoms. [3]
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical and occupational therapy: Tailored exercises improve joint function and reduce pain.
- Surgical options: Joint replacement or repair may be considered for severe cases.
Prevention Strategies

How Can We Prevent Arthritis? Shutterstock Image
A study conducted by the National Library of Medicine found that leading a healthy lifestyle, avoiding excessive repetitive movements, and staying active can diminish the risk of developing arthritis. Regular check-ups facilitate early detection and treatment. [4]
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce inflammation in the body. Avoiding processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive alcohol consumption is also beneficial.
- Protect Joints During Physical Activity: Engage in low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking to strengthen muscles and improve joint flexibility without putting excessive stress on the joints. Using proper techniques and protective gear during physical activities and sports can help prevent joint injuries.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and exacerbate inflammation in the body, potentially increasing the risk of developing autoimmune forms of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in hobbies and activities that promote relaxation can help manage stress levels.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts added strain on the joints, particularly in weight-bearing areas such as the knees, hips, and spine, increasing the risk of developing osteoarthritis. Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of arthritis.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis and can also exacerbate symptoms in individuals already living with arthritis. Quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can help protect joint health and overall well-being.
- Prioritize Joint Health: Pay attention to your body's signals and avoid overexertion or repetitive movements that may strain the joints. Taking breaks during prolonged periods of activity and practicing good posture and ergonomic principles in daily activities can help protect joint health.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of arthritis early on and seeking proper medical advice are crucial steps towards managing this condition effectively. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can achieve significant improvements in their quality of life, navigating the challenges of arthritis with confidence and resilience.
4 Sources
We review published medical research in respected scientific journals to arrive at our conclusions about a product or health topic. This ensures the highest standard of scientific accuracy.
[2] "NIAMS Health Information on Arthritis." National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, 27 July 2023, www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/arthritis.
[3] Schäfer C, Keyßer G. Lifestyle Factors and Their Influence on Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Narrative Review. J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 2;11(23):7179. doi: 10.3390/jcm11237179. PMID: 36498754; PMCID: PMC9736780.
[4] Cooney JK, Law RJ, Matschke V, Lemmey AB, Moore JP, Ahmad Y, Jones JG, Maddison P, Thom JM. Benefits of exercise in rheumatoid arthritis. J Aging Res. 2011 Feb 13;2011:681640. doi: 10.4061/2011/681640. PMID: 21403833; PMCID: PMC3042669.




 This article changed my life!
This article changed my life! This article was informative.
This article was informative. I have a medical question.
I have a medical question.
 This article contains incorrect information.
This article contains incorrect information. This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.
This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.