Introduction
Joint pain affects millions worldwide, significantly impacting life's quality and daily functionality. Understanding its common causes is crucial for effective management and prevention, providing a pathway to a more active and pain-free life.

In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the anatomy of joints, explore age-related joint pain, lifestyle factors, injuries, autoimmune disorders, and environmental influences contributing to joint pain. By gaining insights into these aspects, individuals can make informed decisions to alleviate joint pain and improve their overall well-being.
Anatomy of Joints
According to study joints, the critical connectors within our body enable movement and provide support. From the highly mobile synovial joints like shoulders and knees to the slightly movable vertebrae in our spine, understanding the basic anatomy and function of these joints is essential for recognizing signs of dysfunction and disease. [1]
- Basic Joint Anatomy: Joints are the connections between bones, facilitating movement and flexibility. Understanding the basic anatomy and function of joints provides insight into their vulnerability to pain and injury.
- Types of Joints: There are different types of joints in the human body, including hinge joints (elbows, knees), ball-and-socket joints (hips, shoulders), and pivot joints (neck). Each type plays a specific role in movement and stability.
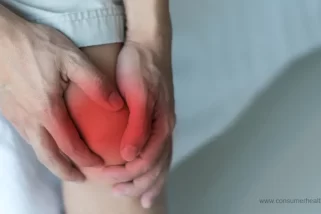
Wear and Tear: Age-Related Joint Pain

How to Get Rid of Old Age Aches and Pains? Shutterstock Image
- Osteoarthritis: Aging leads to the breakdown of cartilage, resulting in osteoarthritis, the most common type of arthritis. Recent research by the Arthritis Foundation, osteoarthritis affects over 32.5 million adults in the United States alone. [2]
- Preventive Measures: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular exercise can help prevent or slow down the progression of age-related joint conditions.
Lifestyle Factors and Joint Pain
This section explores how lifestyle choices such as diet, physical activity, and weight management play pivotal roles in maintaining joint health. Obese individuals, for instance, are four to five times more at risk of developing knee osteoarthritis, making lifestyle modifications a key area of focus.
- Impact of Obesity: Obesity increases the risk of joint pain and osteoarthritis. Research published in the Journal of Obesity found a direct correlation between body mass index (BMI) and the prevalence of knee osteoarthritis.
- Role of Nutrition: A study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology suggests that certain dietary factors, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and anti-inflammatory foods like fruits and vegetables, may help reduce joint pain and inflammation. [3]
Robert McLaughlin II, MD, certified Orthopedic surgeon says that signs and symptoms of joint, shoulder, and muscle pain can vary but often include stiffness, reduced mobility, swelling, warmth in the affected area, and sharp or dull pain during movement or rest. Shoulder pain diagnosis often revolves around assessing these symptoms, along with a thorough physical examination and imaging tests when necessary, to determine the underlying cause such as rotator cuff tendinitis or bursitis.
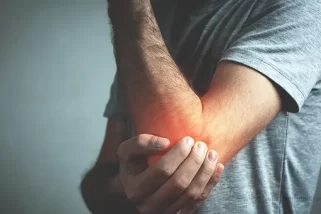
Injuries Leading to Joint Pain
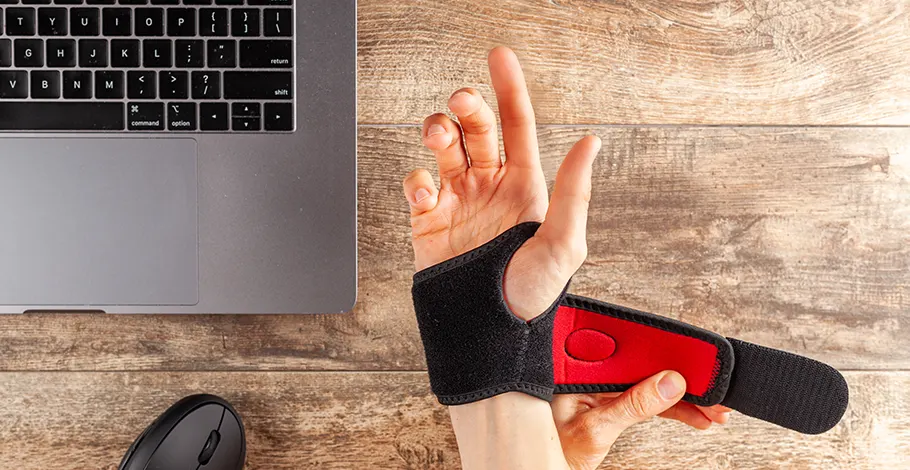

Injuries Leading to Joint Pain. Shutterstock Image
From sports injuries to accidents, trauma to joints can lead to long-term complications. This chapter details common injuries, their effects on joint health, and emphasizes the importance of appropriate rehabilitation and preventative strategies.
- Sports Injuries: High-impact sports and activities can lead to joint injuries such as sprains, strains, and ligament tears. Proper warm-up, stretching, and using appropriate protective gear can reduce the risk of injury.
- Rehabilitation Importance: A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy highlights the importance of proper rehabilitation after joint injuries to restore function and prevent long-term complications.
Autoimmune Disorders and Joint Pain
Understanding the intricate nature of autoimmune disorders necessitates a deep dive into their mechanisms. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and Lupus are autoimmune conditions where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its tissues, causing inflammation and pain in the joints.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), RA affects about 1.5 million Americans, highlighting the vast impact of this condition. Advancements in scientific research have paved the way for innovative treatments, such as biologic response modifiers. These drugs, tailored to target specific parts of the immune system, have shown great promise in reducing the severity of symptoms and improving the quality of life for many patients. [4]
Furthermore, ongoing studies in gene therapy and stem cell research offer a glimpse into a future where these conditions can be managed more effectively or even cured. The integration of these treatments, backed by clinical trials, underlines the importance of personalized medicine in managing autoimmune diseases, ensuring patients receive care that is specifically designed to meet their unique needs.
Environmental and Other Factors
Factors such as climate, workplace ergonomics, and even genetics can influence joint pain. Understanding these can help individuals make informed decisions about managing and potentially mitigating joint pain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the common causes of joint pain is imperative for individuals seeking relief and improved quality of life. From the basic anatomy of joints to the impact of lifestyle factors and autoimmune disorders, this comprehensive guide sheds light on various facets of joint health.
Through awareness and education, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage joint pain effectively. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a balanced diet, and engaging in regular physical activity are key components of joint health maintenance.
Furthermore, advancements in medical research offer hope for individuals suffering from autoimmune disorders such as Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus. Innovative treatments, including biologic response modifiers, gene therapy, and stem cell research, show promise in reducing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
Comparative Analysis
A balanced comparison between conventional and alternative joint pain management methods. Evidence-based insights provide a clear view of the relative safety, efficacy, and potential side effects, guiding readers to make well-informed health decisions.
By arming oneself with this knowledge, it's possible to not only understand the roots of joint pain but to take meaningful steps toward relief and recovery, leading to an enhanced quality of life.
4 Sources
We review published medical research in respected scientific journals to arrive at our conclusions about a product or health topic. This ensures the highest standard of scientific accuracy.
[2] Li Y, Wei X, Zhou J, Wei L. The age-related changes in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:916530. doi: 10.1155/2013/916530. Epub 2013 Jul 22. PMID: 23971049; PMCID: PMC3736507.
[3] Gioia C, Lucchino B, Tarsitano MG, Iannuccelli C, Di Franco M. Dietary Habits and Nutrition in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Can Diet Influence Disease Development and Clinical Manifestations? Nutrients. 2020 May 18;12(5):1456. doi: 10.3390/nu12051456. PMID: 32443535; PMCID: PMC7284442.
[4] Curtis JR, Singh JA. Use of biologics in rheumatoid arthritis: current and emerging paradigms of care. Clin Ther. 2011 Jun;33(6):679-707. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.05.044. PMID: 21704234; PMCID: PMC3707489.




 This article changed my life!
This article changed my life! This article was informative.
This article was informative. I have a medical question.
I have a medical question.
 This article contains incorrect information.
This article contains incorrect information. This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.
This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.