In This Article
Despite its commonness, dehydration is rarely discussed in the media or news. This silent medical ailment occurs whenever someone does not receive the amount of fluid that they need.

They may not be consuming enough water, or they may be dealing with excessive amounts of heat and physical exertion.
No matter what the cause is, dehydration can be a potentially dangerous medical ailment.
What is Dehydration?
Essentially, dehydration occurs when the body is losing more fluids than it takes in.
Water is a necessary nutrient required by the cells and body to function correctly.
In healthy daily life, water is lost through water vapor in breath, stools, urine, or sweat. Whenever water is released from the body, a slight amount of salt is also released.
According to some researchers, there are mainly three types of dehydration.
Hypotonic dehydration is when the majority of substance lost by the body is in the form of electrolytes or sodium [1].
With hypertonic dehydration, individuals may lose some electrolytes, but they are primarily losing water.
Isotonic dehydration is when equal parts of water and electrolytes are lost. The most common form of dehydration is isotonic [2].
What Causes Dehydration?
There is a wide range of conditions that can lead to dehydration. One of the most common ones is heat exposure or excessive exercising. Individuals who have a fever may also lose excessive amounts of water.
Also, patients that have excessive urination, vomiting, or diarrhea may expel more fluid than they can intake.
Injuries like burns, skin infections, or mouth sores can allow water to escape from the body.
Although dehydration can be caused by the excessive release of fluid, it may stem from a lack of fluid consumed. Individuals may be unable to receive enough water or food if they are too young or disabled.
If the individual is unable to drink, they may become dehydrated.
Commonly, this occurs among coma patients, injured individuals, and sick infants.
Likewise, people may not be able to access safe drinking water.
Who is at Risk for Dehydration?
Anyone is at the risk of getting dehydration if they do not consume enough liquid. Athletes may become dehydrated if they do not drink enough fluids after exercising. Whenever the weather heats up, there is always a marked rise in dehydration cases.
Some of the most common causes of dehydration occur in people who are not able to physically obtain liquid. They may have a disability, have mental disorders, or be too young to drink water.
People who are located away from clean water sources or who cannot reach the water source easily may develop dehydration.
What are the Symptoms of Dehydration?
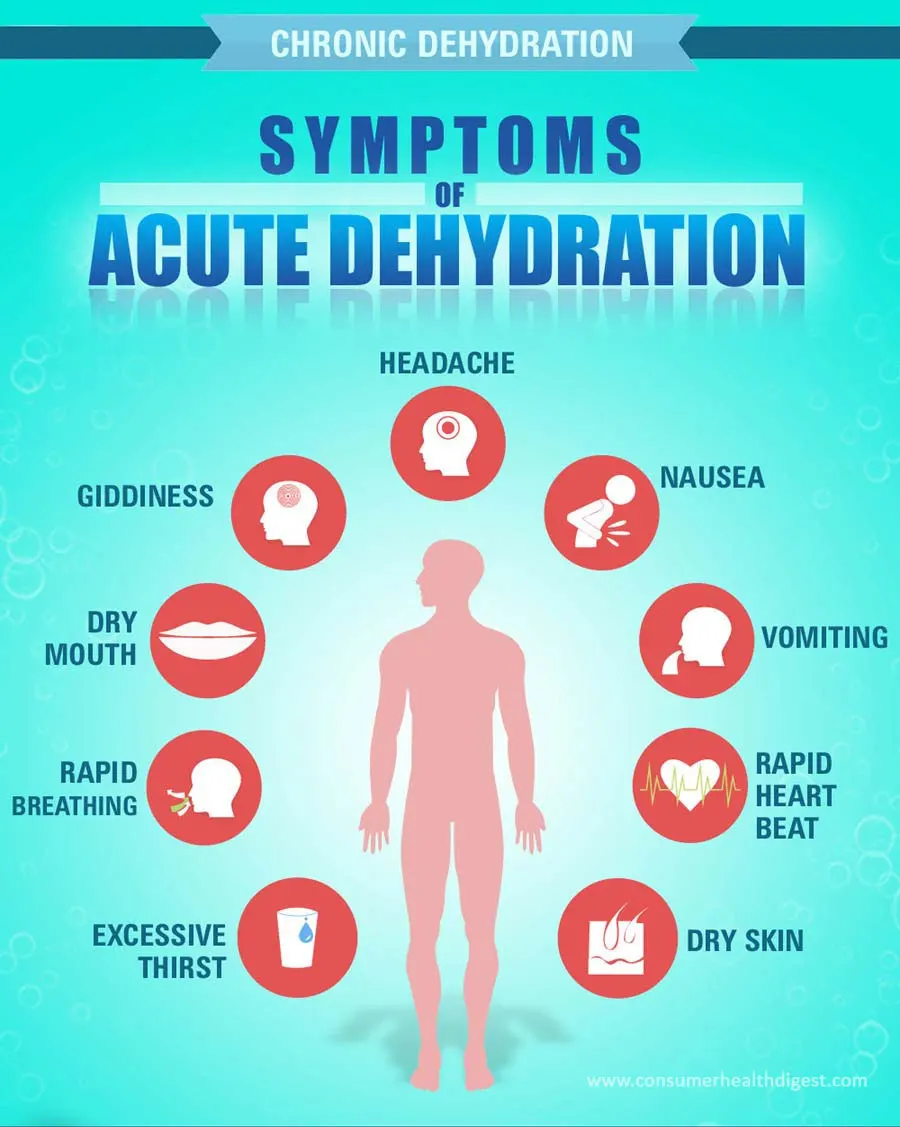
These symptoms can be experienced, if you are dehydrating.
Individuals may not notice that they are becoming dehydrated at first. Many cases of overeating occur because people feel hungry before they feel thirsty. When individuals continue to be dehydrated, they may have the following problems:
- dry mouth
- tongue may swell
- sense of confusion or heart palpitations
- may suffer from feelings of weakness or dizziness
In the initial stages, they may also feel thirsty all the time and develop water retention.
If the condition progresses further, the dehydration symptoms may become more severe. The individual may be incapable of sweating or feel sluggish.
Without adequate liquid, the urine output will decrease, and they may faint easily.
Likewise, the urine color may become dark yellow or amber if someone is dehydrated.
How Dehydration is Linked with Water Retention Problems?
It may seem counter-intuitive, but water retention often occurs in the initial stages of dehydration.
As the body loses fluids, it will try to make up for the loss by conserving any remaining. It will make urine output decrease and remove excess fluid from any stool.
Instead of processing liquid out of the body, the water is reabsorbed into the tissue.
When this occurs, someone will suffer from the swelling and pain caused by water retention. If the dehydration progresses, it may make the water retention go away.
Unfortunately, the water retention will only go away in this instance due to severe dehydration.
The only way to remove the medical risks, water retention, and dehydration permanently is to begin drinking more fluids.
How Is Dehydration Diagnosed?
A doctor typically diagnoses dehydration. They may take vital signs like the heart rate, blood pressure, and check for signs of a fever.
Also, doctors will often use blood or urine tests to figure out the cause of the dehydration.
A urine test will also show the color and clarity of the urine. Any ketones present will indicate that the body is dehydrated.
If there is a significant amount of protein present in the urine, it could be a sign that there is an underlying kidney problem.
Blood tests will look for the amount of salt and sugar available.
This will indicate to the doctor how well the kidney is functioning. In addition, a blood test may show if there are any infections that could be causing the dehydration.

Health Professionals can help you to treat dehydration.
Preventing Dehydration
Since dehydration can be a dangerous medical condition, individuals should always work to prevent it from happening. They can drink extra fluid before working out or being outside for long periods.
If the weather is scorching, they may want to avoid being outside.
Also, avoiding diuretics like coffee and alcohol can help prevent dehydration.
In the case of disabled, elderly, or young individuals, their caretaker can make sure that drinking water is readily available.
How To Treat Dehydration?
With adults, dehydration can often be treated at home. They should drink additional water or electrolyte drinks. Ice chips or popsicles can also increase someone's fluid intake.
If the individual has been exposed to too much heat, they can be cooled through air conditioning, fans, spray bottles, or ice water.
When dehydration symptoms is serious, a doctor may use an IV to speed up the rehydration process.
Dehydration can be a serious illness. It can cause heart palpitations, water retention, and fainting.
Although the most natural treatment is through prevention, individuals can receive medical assistance to speed up recovery.
2 Sources
We review published medical research in respected scientific journals to arrive at our conclusions about a product or health topic. This ensures the highest standard of scientific accuracy.
[2] Water, Hydration and Health: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2908954/





 This article changed my life!
This article changed my life! This article was informative.
This article was informative. I have a medical question.
I have a medical question.
 This article contains incorrect information.
This article contains incorrect information. This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.
This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.