Dehydration occurs when the body excretes more water than you can consume. This can happen for numerous reasons, such as excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, or not drinking enough liquids.
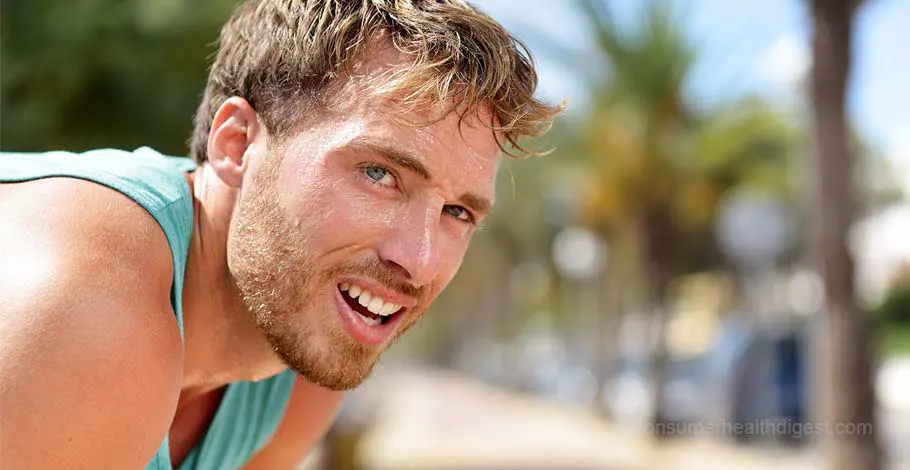

Dehydration symptoms range from mild to severe and may lead to serious health complications if left untreated. Therefore, understanding the warning signs of dehydration is critical in avoiding such outcomes. This article talks about how to tell if you are getting dehydrated and what to do about it.
Here are some common signs of dehydration:
1.Thirst
Thirst is one of the primary signs that your body is dehydrated. Your body will try to signal you by making you thirsty that it needs more fluids by making you experience thirst. Therefore, it's essential to hydrate as soon as possible when feeling thirsty to prevent dehydration from worsening further.
2.Dry Mouth and Throat
Dry mouth and throat are common signs of dehydration and can occur for many reasons. As your body loses water, it produces less saliva, leading to a dry and sticky sensation in your mouth and throat, making swallowing or speaking difficult.
3.Dark Urine
Dark urine is a sign of dehydration and should serve as a warning that your body isn't getting enough fluids. Dehydrated kidneys produce less urine, leading to darker than usual urine with either yellow or amber hues. If you notice your urine looking darker than usual, consider whether you may be dehydrated.
4.Fatigue and Dizziness
Dehydration can also cause fatigue and dizziness due to a body that lacks fluids, making you inactive. Without enough oxygen and nutrients, dehydration leads to fatigue and weakness from anemia low blood pressure. Dizziness may occur from this drop in blood pressure which can occur when dehydrated.
5.Headaches
Headaches often indicate dehydration when your body doesn't get enough fluids. Dehydration reduces blood flow to the brain, causing blood vessels to constrict and create headaches - often described as a dull, throbbing pain that radiates throughout the head.
6.Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps are another common indication of dehydration. Dehydration causes your body to lose essential electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium that support proper muscle function - leading to painful cramps in the affected areas.
7.Rapid Heartbeat
Ticking hearts, also known as tachycardia, is another sign of dehydration. Dehydrated individuals typically experience decreased blood volume, which causes their hearts to work harder to circulate blood throughout their body - leading to an elevated heart rate or rapid beats.
8.Sunken Eyes
Sunken eyes are a less commonly recognized sign of dehydration, but they indicate your body lacks water. Dehydrated individuals typically exhibit symptoms such as puffy and darkened skin around their eyes in an attempt to conserve water by decreasing blood flow to particular areas. When this occurs, the skin around these parts becomes sunken and inebriated.
Common Causes of Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body loses more fluids than it takes in. Here are some common reasons for dehydration:
- 1.Excessive Sweating: Sweating is your body's way of controlling temperature. However, excessive sweating - such as during intense exercise or hot weather - can cause the body to lose more fluids than it takes in, leading to dehydration.
- 2.Inadequate Fluid Intake: If you fail to drink enough fluids, your body won't have enough for proper function. This can happen if you aren't getting enough water or consuming fluids that dehydrate you more rapidly, such as caffeine or alcohol.
- 3.Vomiting and Diarrhea: Vomiting and diarrhea can cause significant fluid loss, leading to dehydration as the body's ability to absorb fluids and nutrients is impaired.
- 4.Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions can increase your likelihood of dehydration. These include diabetes, kidney disease, and adrenal gland disorders.
- 5.Environmental Factors: Environmental elements like high altitude or dry air can exacerbate fluid loss leading to dehydration.
How to Deal with Dehydration
Here are four strategies for dealing with dehydration.
1.Hydrate Regularly
Drinking plenty of fluids is one of the simplest and most efficient ways to prevent dehydration and treat it effectively. Water is ideal, but other fluids such as fruit juices, sports drinks, and broth can also be consumed. However, it's important to remember that caffeine and alcohol worsen dehydration; thus, avoiding them is best.
If you are feeling dehydrated, drinking fluids is the best way to replenish your body. It's best to drink fluids throughout the day rather than waiting until thirsty because thirst may not always accurately indicate dehydration, particularly in older adults.
2.Consume Foods with High Water Content
Eating foods high in water content can help combat dehydration. Examples include fruits like watermelon, oranges, and grapes and vegetables like cucumbers, lettuce, and tomatoes. They provide essential water, vitamins, and minerals your body needs to replenish itself.
3.Stay Cool
Staying cool during hot weather or physical activity is essential to prevent dehydration. Wear loose-fitting, lightweight clothing and avoid outdoor activities during peak heat hours. When exercising, drink fluids before, during, and after your session to prevent dehydration. You can also use a sports drink that contains electrolytes to replace lost salts and minerals from sweat.
4.At-Home IV Treatment
Dehydration can become so severe that at-home IV treatment may be necessary. This involves administering fluids and electrolytes directly into your bloodstream via an IV, which can be done conveniently at home with the assistance of a medical professional or nurse.
During at-home IV treatment, a medical professional will assess your hydration status and place an IV line in your arm or hand. They then administer fluids and electrolytes through the IV to help rehydrate your body. The length of treatment depends on how severe the dehydration is. It's essential to note that at-home IV treatment should only be undertaken under the guidance of a medical professional and never attempted without proper training and equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is dehydration?
A: Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it intakes. This can be due to factors like sweating, urinating, diarrhea, vomiting or not drinking enough fluids.
Q: How is dehydration diagnosed?
A: Dehydration is typically diagnosed through symptoms, physical exam findings and laboratory tests such as blood tests or urinalysis.
Q: How is dehydration treated?
A: Dehydration usually requires replacing lost fluids and electrolytes through oral or intravenous administration of electrolyte solutions or sports drinks, or in severe cases IV fluids.
Q: What is an IV treatment for dehydration?
A: An IV treatment involves administering fluids and electrolytes directly into the bloodstream through an IV catheter.
Q: How does an IV treatment for dehydration work?
A: An IV treatment for dehydration works by providing the body with essential fluids and electrolytes that support proper functioning. Typically, this solution contains water, sodium, potassium and other electrolytes in a balanced ratio.
Q: What are the advantages of IV treatment for dehydration?
A: An IV treatment can quickly restore fluid and electrolyte balance, provide relief from symptoms such as nausea or headache, and help protect against serious dehydration complications.
Q: Can I receive IV treatment for dehydration at home?
A: In certain circumstances, a healthcare provider may be able to administer an IV treatment in the comfort of one's own home. However, this depends on the individual's individual needs and medical condition.
Conclusion
Dehydration is a serious medical condition that can have numerous negative consequences, from headaches and confusion to death. To avoid dehydration and maintain good health, it's essential to recognize its signs and take preventive measures. By staying hydrated, we can keep our bodies functioning properly and maintain good health.






 This article changed my life!
This article changed my life! This article was informative.
This article was informative. I have a medical question.
I have a medical question.
 This article contains incorrect information.
This article contains incorrect information. This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.
This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.