Nausea is one of the most annoying pregnancy related conditions, and definitely one of the most common. Many women suffer from this sickness in one form or another, caused by the increasing levels of hormones circulating in the blood. Nausea during pregnancy, commonly referred to as morning sickness, affects a significant number of pregnant individuals, typically during the first trimester. It's believed to be caused by the increase in pregnancy hormones, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and estrogen. [1]
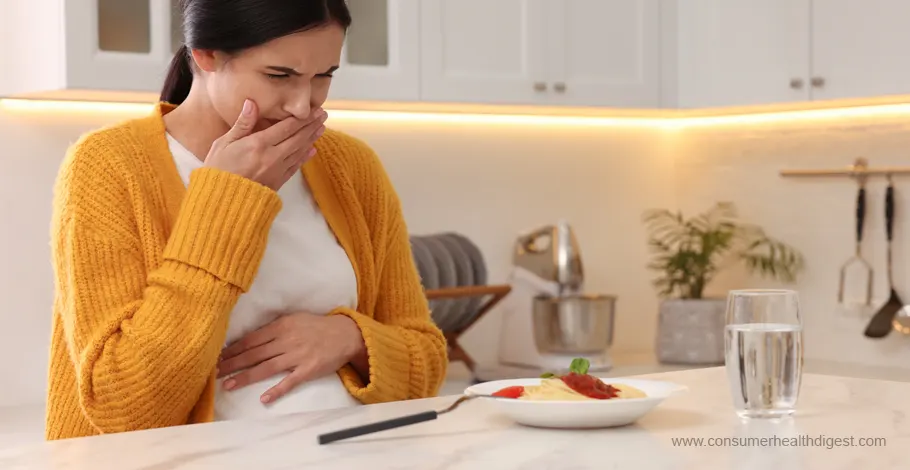

While called “morning sickness,” the discomfort can occur at any time of the day and varies greatly among pregnancies. Mild to moderate nausea is considered a normal part of pregnancy, but severe cases, known as hyperemesis gravidarum, require medical attention. Eating small, frequent meals, avoiding foods with strong odors, and staying hydrated are recommended strategies for managing nausea during pregnancy. It's a condition that underscores the body's complex response to pregnancy, and while challenging, it's often seen as an early sign of a progressing pregnancy.
What is Nausea in pregnancy??
Nausea often termed as morning sickness, is a common symptom experienced by many pregnant individuals, marked by a persistent feeling of queasiness or urge to vomit. This condition is most prevalent in the first trimester of pregnancy but can extend beyond this period in some cases. Although the exact cause is not fully understood, it is attributed to the rapid increase in hormones such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and estrogen. Despite its discomfort, morning sickness is generally considered a normal part of pregnancy and a sign that the pregnancy hormones are functioning as expected. [2]
Causes
Many theorize that the rise in the pregnancy hormone hCG, one part of which at a microscopic level resembles thyroid hormone, causes nausea in a way similar to the way hyperthyroidism can cause it. Others think it’s the estrogen, which is responsible for increasing blood flow to the taste buds and affects taste and cravings negatively as well as positively. Since taste is almost identical to smell, this would explain the reason some smells set off a wave of nausea. Another reason for nausea is the rapid expansion of the uterus. [3]
Surprisingly, some expectant women never suffer from nausea during their whole pregnancy period. Conversely, many women suffer greatly; even they need to get admitted into hospital immediately to keep hydrated with IV solutions. When nausea gets too bad, it is referred as Hyperemesis Gravidarum, which is a vicious cycle: nausea causes dehydration, and vice versa dehydration degrades your current stage of nausea, and further this nausea causes further dehydration. This sequence can be broken by rehydrating with simple overnight IV, which is often enough to get a woman stable enough to begin eating again. [4]
How Long The Symptoms will Lasts?
Nausea is the most common complaint of the first three months of pregnancy. One-third of pregnant American women are affected with vomiting or digestive disturbance but it usually stops at the end of the first trimester. Nausea actually can be any time and can even last all day long (and all night too). Usually when the amount of rising hCG plateaus (at about ten weeks), the nausea subsides. Improvement will be gradual: the nausea and vomiting won’t clear up dramatically in one day. Good days will gain over bad ones until there are fewer and fewer bad days and the nausea finally disappears. There are exceptions, with lingering into the second trimester, but this time the nausea is much more tolerable. [5]
Management of Pregnancy Nausea
According to Dr. Matthew Casavant, Board Certified OB-GYN, some patients find relief by consuming ginger or taking vitamin B6 supplements. In more severe cases, safe medications can be prescribed. It’s crucial to avoid letting the stomach get too empty or too full and to consider prenatal vitamins at bedtime to minimize nausea.
There are few feelings as bad as the feebleness of nausea, and on one point the practitioners find reassurance in this misery because it means the hormones are intense and the pregnancy is perhaps strong. But the nutritional shutdown is never normal. The dehydration is never normal. And it happens that a lot of the suffering goes unimproved in spite of the practitioner's best efforts. Both the non-prescription remedy and a handful of prescription drugs help to struggle with nausea. Emetrol, that is an over- the- counter mixture of sugar syrups and phosphoric acid, which acts as the soother for the actual wall of the gastrointestinal tract to reduce nausea. Here are a few other ways of managing your pregnancy nausea. [6]
- Do not allow yourself to get too hungry. Eat smaller, more frequent meals and snacks more often. An empty stomach can cause nausea more badly.
- Do not force yourself to eat foods that make you gag.
- Choose stomach friendly foods like yogurt (a good source of vitamins B), low-fat, and high carbohydrate foods (starches).
- Do not overeat. Having a stuffed belly will only add to your feelings of nausea.
- Do not have fluids on mealtimes. Some women find that eating and drinking at the same time can trigger nausea. Just make sure you make up for those lost fluids at the other tomes of the day, since dehydration can also cause nausea.
- Watch when you are taking your prenatal vitamins. If you are taking it on an empty stomach, you are asking for trouble. Try making it in the middle of a meal instead.
- Prescribe Compazine, Phenergan, Tigan, or Reglan.
- Prescribe Zofran.
- Parental hydration is an important issue. Parental hydration word refers to administering by intravenous route (i.e., by an IV infusion). The dehydration from nausea and vomiting can make nausea worse. Usually one night stay in the hospital with physiologic solution by IV can redeem a severe nausea.
Additional Tips to Manage Pregnancy Nausea
Here are some more tips to coping with your nausea:
- Try until you find one or more foods that tempt you. You may discover that certain categories of foods –salty, bitter, crunchy, sweet, hit, cold, or thick, etc. also appeal.
- Avoid greasy, spicy foods as well as hard to digest food such as sauces, onion rings and fatty fried foods.
- Avoid pants with belts and other types of tight-fitting clothing. They will only add to your discomfort.
- Carry around a piece of lemon or mint leaves or grated ginger root. Some ladies find that smelling one of them helps to settle their heaving stomach.
- Mid-Morning snack of a banana helps many women.
- Drink very hot or very cold liquids: the extreme temperatures may make you feel better.
It is not easy to think that if your feeling so ill due it must mean there’s something wrong with your pregnancy, but quite opposite is true: Studies have shown that women with little or no morning sickness with nausea and vomiting are two to three times as likely to miscarry as those who are feeling totally wretched. What’s more, they’re less likely to experience a premature birth.
Consult a medical professional
The information provided herein is designed for educational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical advice. The experiences and strategies mentioned regarding nausea during pregnancy, including symptoms and management, may vary from individual to individual. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or medical expert to discuss your specific situation, particularly if you experience severe or persistent nausea, to ensure the health and safety of both you and your baby. The guidance of a medical professional is crucial in making informed decisions about your pregnancy and health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Although it can be an uncomfortable and sometimes debilitating experience, it is generally considered a normal part of pregnancy. Various strategies can help manage the symptoms, from dietary changes to prescribed medications. Importantly, those experiencing severe or persistent nausea should consult a healthcare provider to ensure both their well-being and that of the developing fetus. The journey of pregnancy, with its myriad of changes, underscores the importance of understanding and addressing such common challenges, ensuring a safer and more comfortable experience for expectant mothers.
6 Sources
We review published medical research in respected scientific journals to arrive at our conclusions about a product or health topic. This ensures the highest standard of scientific accuracy.
[1] "Mother To Baby | Fact Sheets [Internet]." Nausea and Vomiting in Pregnancy (NVP). Organization of Teratology Information Specialists (OTIS), Feb. 2022, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK582541/#:~:text=About%2080%25%20of%20people%20who,peaks%20between%207%2D12%20weeks.[2] Liu, Chuan, et al. "Emerging Progress in Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy and Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Challenges and Opportunities." Front. Med., vol. 8, 2021, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.809270.
[3] (uk), National Guideline Alliance. Management of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), 2021, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK573942.
[4] Northrop, Vivienne. "Cambridge-led study discovers cause of pregnancy sickness – and potential treatment - Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre." Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre, 14 Dec. 2023, cambridgebrc.nihr.ac.uk/cambridge-led-study-discovers-cause-of-pregnancy-sickness-and-potential-treatment.
[5] Einarson A, Maltepe C, Boskovic R, Koren G. Treatment of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy: an updated algorithm. Can Fam Physician. 2007 Dec;53(12):2109-11. Erratum in: Can Fam Physician. 2019 Jan;65(1):8. PMID: 18077743; PMCID: PMC2231543.
[6] Heitmann K, Svendsen HC, Sporsheim IH, Holst L. Nausea in pregnancy: attitudes among pregnant women and general practitioners on treatment and pregnancy care. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2016;34(1):13-20. doi: 10.3109/02813432.2015.1132894. Epub 2016 Feb 8. PMID: 26854395; PMCID: PMC4911029.





 This article changed my life!
This article changed my life! This article was informative.
This article was informative. I have a medical question.
I have a medical question.
 This article contains incorrect information.
This article contains incorrect information. This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.
This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.